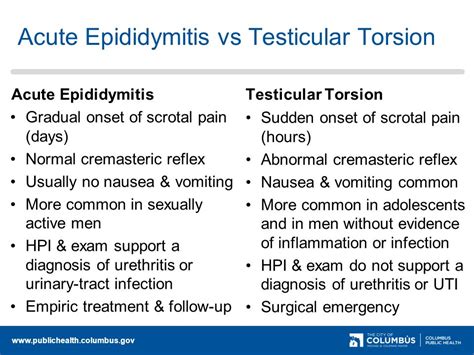
test for torsion testis|testicular torsion vs epididymitis signs : traders Testicular torsion. During testicular torsion a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that brings blood to the scrotum, the loose bag of skin under the penis that .
Resultado da 16 de fev. de 2023 · A empresa Garena, produtora e distribuidora do Free Fire, divulgou nesta quinta-feira (16) seu novo site oficial para resgate de Codiguin FF, o Rewards .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Mata, Onaji Yume wo Miteita. Secret Class online para ler o mangá em Português (PT-BR) grátis com todos os capítulos completos e sem anúncios atrapalhando!
Prehn's sign is a clinical finding that helps clinicians determine whether testicular pain is caused by epididymitis or testicular torsion. A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of .
Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the .Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . Testicular torsion. During testicular torsion a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that brings blood to the scrotum, the loose bag of skin under the penis that .
testicular torsion vs epididymitis signs
Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.
In 2013, a simple risk score for the diagnosis of testicular torsion was developed by Barbosa and colleagues. 4 The authors called it the Testicular Workup for Ischemia and Suspected. Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, .
Investigations. The diagnosis of testicular torsion is a clinical one, therefore any suspected cases should be taken straight to theatre for scrotal exploration.. However, in cases with sufficient equipoise, Doppler ultrasound . Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic .
testicular torsion survival rate
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage. Find out what causes this .
Testicular torsion can occur at any age but commonly occurs soon after birth or between the ages of 12–18 years with a peak in incidence at age 13–14 years. . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with grade 3 bleeding (major bleeding that requires multiple hemoclips and sessions of hemocoagulation) required . Testicular torsion occurs in teenage boys aged 13-18 years. This is found to happen in around 1 in 4,000 young men. Newborn babies and younger children sometimes develop this problem. It is uncommon over the age of 25 but does occur sometimes in older adults and can occur at any age.Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.↑ Blaivas, M, et al. Emergency evaluation of patients presenting with acute scrotum using bedside ultrasonography. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2001; 8(1):90-93. ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8. ↑ Gordon J, Rifenburg RP. . Spermatic Cord .
testicular torsion signs on examination
Torsion of the testicular appendages is considered the most common cause of acute scrotal pain in prepubertal children and may even be the single most prevalent cause of pediatric orchalgia.[1] Therefore, it should be included in the differential diagnosis for any male presenting with an acute scrotum, particularly in the pediatric age group.[1] Two testicular . Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and definitive management are the keys to avoid testicular loss. All prepubertal and young adult .
1: Epididymis 2: Head of epididymis 3: Lobules of epididymis 4: Body of epididymis 5: Tail of epididymis 6: Duct of epididymis 7: Deferent duct (ductus deferens or vas deferens). Prehn's sign (named after urologist Douglas T. Prehn) [1] is a medical diagnostic indicator that was once believed to help determine whether the presenting testicular pain is caused by acute .A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).
A torsion test is a mechanical testing method that evaluates the properties of materials or devices under stress caused by angular displacement. During a torsion test, a specimen is subjected to a twisting or torsional force, which induces a torque. This test is used to measure various mechanical properties of materials, including their modulus of rigidity, shear stress, .
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic Test for Testis Torsion in Pediatric Acute Scrotum: A Prospective Comparison to Gold Standard Diagnostic Test Study. J Urol .American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, hernia, scrotal trauma, testicular torsion, testicular tumor, and torsion of testicular appendices.The recommendations on management of testicular torsion are based on the European Association of Urology (EAU) guideline Paediatric urology [Radmayr, 2021], the Royal College of Surgeons (RCS) joint publications Asymptomatic scrotal swelling, commissioning guide [] and Management of paediatric torsion, commissioning guide [], and expert opinion in review .Testicular torsion is generally treated with surgery, which is done as soon as possible. For the best chance of preventing permanent damage your testicle, surgery should be done within 6 hours from when the pain started. During the operation, the surgeon will make a small cut in your scrotum and untwist the spermatic cord. They will then stitch .
The appendix testis is a small appendage of normal tissue that is usually located on the upper portion of the testis. The appendix epididymis is a small appendage on the top of the epididymis (a tube-shaped structure connected to the .Testicular torsion must be considered in any patient who complains of acute scrotal pain and swelling. Torsion of the testis is a surgical emergency because the likelihood of testicular salvage . The cremasteric reflex has been reported to be absent in 100% of cases of testicular torsion, making it a potentially useful sign in this diagnosis. However, a significant number of case reports and small case series exist, demonstrating that the test is not 100% specific, and the reflex can be present in cases of testicular torsion. The test can show if you have testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow. If ultrasound with color Doppler shows lower blood flow to a testicle than is typical, the testicle is twisted. If blood flow is higher than typical, this can help confirm that you have epididymitis.
testicular torsion prognosis

Torsio testis bisa dialami oleh laki-laki pada usia berapa pun, Torsio Testis. Torsio testis adalah kondisi ketika testis atau buah zakar terpelintir sehingga menimbulkan nyeri hebat pada testis. Torsio testis bisa dialami oleh laki-laki pada usia berapa pun, tetapi paling sering terjadi di usia kurang dari 25 tahun. Doppler flow in the symptomatic testis may be absent, have abnormally high resistance, or be reduced. Testicular torsion, caused by twisting of the testis on the spermatic cord, is the most common cause of absent testicular flow, particularly in adolescent boys . The most common cause of torsion is bell clapper deformity, in which the abnormal .
Testicular torsion, or twisted testicle, can be extremely painful. . A healthcare professional may also test the patient’s cremasteric reflex, which is highly effective in helping diagnose .
Testicular torsion has an annual incidence of approximately 1 in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. 1 It is more common in children and adolescents, and delayed repair can result in the loss of .This video contains a visual explanation of testicular torsion, aimed at helping students of medicine and healthcare professionals prepare for exams. Written.Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours . See a doctor right away if you think you have .
Torsion of the appendix testis is a twisting of a vestigial appendage that is located along the testicle. This appendage has no function, yet more than half of all boys are born with one. Although this condition poses no threat to health, it can be painful. Usually no treatment other than to manage pain is needed.
testicle torsion prognosis
how to avoid testicular torsion
10 de mai. de 2020 · Portal do Zacarias. Um monte de imbecil falando que ele tá errado, ele tá errado nada já pensou se no lugar daquele boi fosse a filha dele ou filho ela mata qualquer coisa que passe na frente se estiver com fome,matar um bixo que pode ameaçar outra vida não é problema muito menos errado,ela ia se alimentar tudo bem ia sim,ela ia .
test for torsion testis|testicular torsion vs epididymitis signs